Glass Machining: CNC vs Traditional Methods Explained
发布时间:
2025-06-07 15:16
来源:
Huize Glass
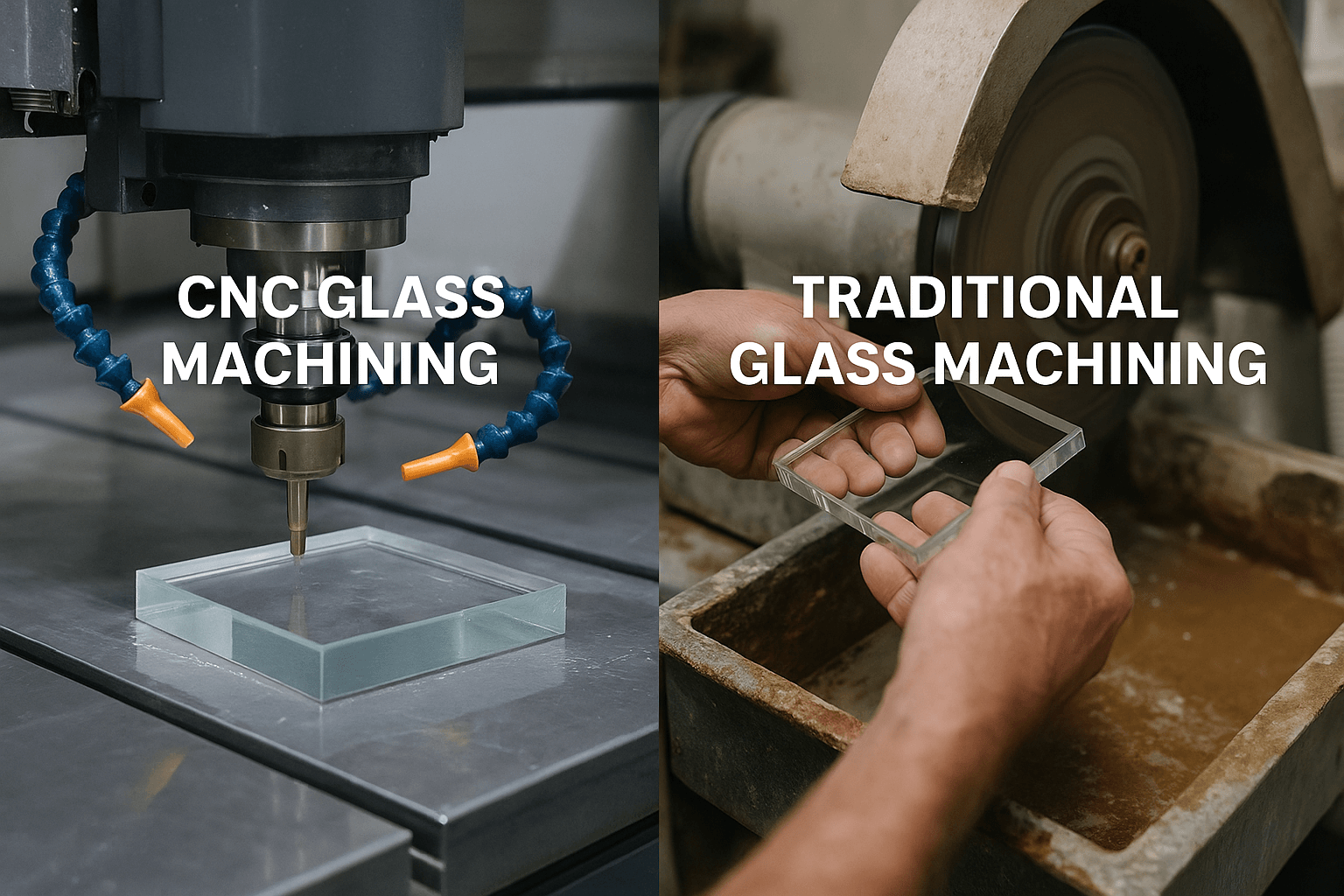
Key Highlights
- CNC glass machining achieves unparalleled high precision and tight tolerances, making it ideal for intricate designs and complex shapes.
- Traditional glass machining employs manual methods to shape glass, ensuring versatility but sometimes compromising precision.
- CNC machines cater to diverse glass types, including fused silica and borosilicate, to meet the highest industry standards.
- Turnaround time and project intricacy vary significantly between CNC machining and traditional approaches.
- Selection between CNC and traditional methods depends on requirements like custom glass fabrication, machining process needs, and budget constraints.
Introduction
Glass machining has evolved substantially, replacing traditional manual methods with cutting-edge technologies like CNC machining. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) glass machining streamlines the manufacturing process, offering unmatched precision and repeatability. It excels at transforming raw glass into components with complex designs, tight tolerances, and high precision. While traditional techniques still hold relevance, the machining process offered by CNC methods has increasingly gained traction among industries like electronics, optics, and aerospace. Understanding their differences empowers you to choose the best method for your application.
Key Differences Between CNC and Traditional Glass Machining
CNC glass machining relies on automated programming and high-precision equipment to deliver consistently accurate results. It produces intricate shapes like bevels, grooves, and chamfers that are difficult to achieve manually. By contrast, traditional glass machining is rooted in manual craftsmanship, making it more accessible but less repeatable for complex projects.
With CNC machining, tight tolerances and precision are guaranteed, allowing it to outperform traditional methods when complex designs or optical applications are required. However, traditional methods may serve better for simpler glass parts or artisanal creations.
Process Overview: Automation vs Manual Techniques
The CNC machine automates the glass machining process, allowing manufacturers to create intricate designs with ease. Programs such as G-code manage setup and execution, ensuring accuracy at every stage. Automation reduces human error, eliminates inconsistencies, and operates 24/7 with limited supervision.
Conversely, manual techniques rely heavily on skilled operators for setup and precision. Tasks like engraving and shaping demand significant expertise but lack the repeatability of automated systems. This method is most effective for small-scale or unique projects.
Precision, Speed, and Complexity of Machined Parts
Achieving high precision is a central tenet of CNC machining. The process enables tight tolerances essential for drilling, milling, and custom glass fabrication on glass components. By contrast, manual methods may lack the consistency needed for exact specifications.
Speed is another differentiator. CNC technology completes complex projects in record time, benefiting industries with strict deadlines. In traditional machining, slower processes are better suited for less demanding tasks.
CNC machines effortlessly produce intricate, complex shapes, revolutionizing the capabilities for optical components, grooves, and custom glass designs. Manual techniques struggle to replicate such detail and are generally limited to simpler configurations. This stark contrast underscores the advantages of precision machining in modern applications.
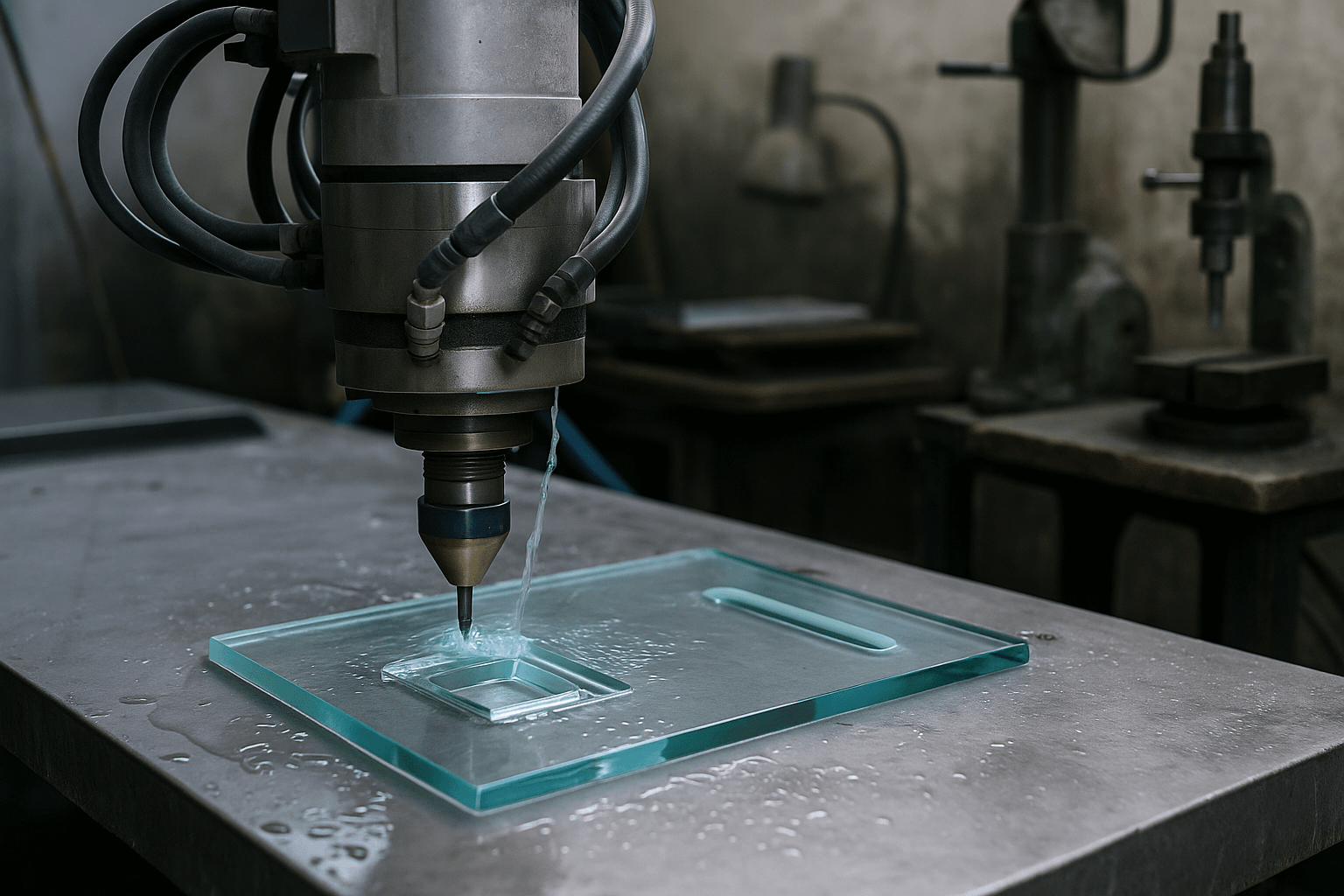
Explanation of CNC Glass Machining Process
Utilizing advanced CNC glass machining processes, manufacturers achieve remarkable precision in glass fabrication. This method employs computer-controlled machines for drilling, milling, and cutting, ensuring tight tolerances across various glass types. Through sophisticated computer-aided design (CAD) software, intricate designs and complex shapes can be created efficiently. The automated nature of CNC allows for high-speed production, significantly reducing setup time and human error, while adhering to the highest industry standards for quality and endurance in the finished glass parts.
1. Overview of Traditional Glass Machining Techniques
Traditional glass machining techniques primarily involve manual processes, employing tools like lathes, grinders, and saws to shape and manipulate various glass types. These methods allow artisans to create intricate designs and custom glass fabrication by hand, though precision can vary. Operators often rely on their skills to ensure quality, adhering to industry standards. Common practices include drilling, milling, and laser cutting, all of which enable the production of high-quality optical components, albeit with limitations in speed and tight tolerances compared to CNC machining.
2. Key Differences Between CNC and Traditional Methods
CNC machining offers a level of automation that sets it apart from traditional methods. Automated processes ensure high precision and repeatability, enabling the production of complex shapes and tight tolerances that may be challenging to achieve manually. In contrast, traditional techniques often rely on skilled labor, which can introduce variability and limit the complexity of designs. While CNC glass machining excels in fabricating optical components with meticulous accuracy, the conventional approach may still hold appeal for custom glass fabrication where hands-on craftsmanship is valued.
3. Advantages of CNC Glass Machining
CNC glass machining offers several advantages that elevate it above traditional methods. Enhanced precision enables the creation of complex shapes and intricate designs, allowing for the production of high-quality optical components and durable glass parts. Faster setup and reduced operational time lead to increased efficiency, catering to tight tolerances across various glass types. Additionally, the process is designed to meet the highest industry standards, ensuring consistent results that align with sophisticated custom glass fabrication needs.
4. Limitations of Conventional Glass Machining
Conventional glass machining presents several notable limitations. Manual techniques often struggle to achieve tight tolerances, leading to variations in the final product's quality. Additionally, the complexity of designs and intricate shapes can be challenging to replicate consistently, particularly with various glass types. The slower processing speed hampers efficiency, ultimately increasing labor costs and turnaround times. As optical components require high precision, conventional methods may fall short of meeting the highest industry standards, affecting both durability and structural integrity.
5. Cost Analysis: CNC vs Traditional Glass Machining
A thorough cost analysis reveals significant differences in expenditure between CNC and traditional glass machining. CNC machines, while initially more expensive, offer savings in labor and higher precision, which reduce material waste and rework costs over time. Conversely, traditional methods often involve more manual processes, leading to increased labor costs. Understanding these financial implications can help businesses make informed decisions based on their specific requirements, the complexity of glass parts needed, and the desired production scale.
6. Precision and Accuracy: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Precision and accuracy define the quality of glass machining, varying significantly between CNC and traditional methods. CNC glass machining excels in producing components with tight tolerances, ensuring that complex shapes and designs are replicated with high precision. Manual techniques, while skilled, often lead to variations due to human factors, impacting the overall consistency of produced glass parts. Ultimately, for projects requiring utmost precision, CNC offers advanced capabilities that adhere to the highest industry standards, making it the preferred choice for intricate applications.
7. Material Compatibility: Which Method Wins?
When evaluating material compatibility, CNC machining excels with its ability to handle a wide range of materials with precision. In contrast, traditional methods may be limited in versatility, making CNC the preferred choice for complex and diverse glass machining applications.
8. Speed and Efficiency in Glass Machining
Speed and efficiency play crucial roles in the glass machining landscape. CNC glass machining significantly enhances production timelines, allowing for rapid setup and execution of complex designs. Automation leads to the ability to process high volumes while maintaining tight tolerances. Traditional methods, although valuable, often demand more time for manual operations like drilling and milling. As a result, CNC techniques emerge as the preferred choice for industries requiring precision and streamlined workflows, thus meeting the highest industry standards consistently.
9. Future Trends in Glass Machining Technologies
Advancements in glass machining technologies are set to revolutionize the industry. Integration of AI and machine learning in CNC glass machining will enhance precision and optimize setups for complex designs. The rise of automation allows for quicker adaptations to various glass types, promoting rapid production of high-precision glass parts. Additionally, the exploration of new materials, like advanced silica composites, may further improve functionality in optical components and complex shapes, ensuring adaptability to the highest industry standards.
10. Choosing the Right Method for Your Project Needs
Selecting the appropriate glass machining method hinges on various project requirements. For intricate designs with tight tolerances, CNC glass machining excels, providing high precision and efficiency essential for optical components and complex shapes. Conversely, traditional techniques may suit projects that necessitate manual skill and craftsmanship, particularly for simpler designs. Evaluating the type of glass, desired thickness, and cost considerations will guide you in making an informed choice, ensuring your project adheres to the highest industry standards.
Common Applications for CNC and Traditional Glass Machining
Both CNC and traditional glass machining find applications across varied sectors, catering to industrial, scientific, and aesthetic needs. CNC glass machining is pivotal for producing optical components like lenses and prisms that demand tight tolerances.
Traditional methods, on the other hand, suit decorative glass items and basic glass parts. Glass types—like silica and soda-lime—shape the choice between CNC machining and traditional techniques, determined by complexity requirements and practical uses.
Industrial, Scientific, and Custom Projects
Diverse fields rely on both CNC and traditional glass machining for specific requirements. Below are examples illustrating their utility:
Scientific Instruments: Precise machining forms lenses and prisms, ensuring consistent diameter, width, and thickness suitable for optical experiments.
Industrial Manufacturing: CNC machining aids with complex geometries and silica components, like reference frames in semiconductor setups.
Custom Glass Fabrication: CAD-driven processes allow tailored designs like intricate bevels or high-strength applications.
Aerospace and Defense: Lightweight yet durable glass parts, such as polished mirrors, underscore CNC's adaptability for advanced projects.
Whether crafting fine optical components or robust protectors, glass machining supports high standards across applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between CNC and traditional glass machining is essential for selecting the right method for your project. Each technique has its own strengths and weaknesses, from precision and speed to complexity and application. CNC machining shines in scenarios requiring high accuracy and intricate designs, while traditional methods may be more suitable for simpler tasks. As you navigate your options, consider your specific needs, whether they relate to cost, turnaround time, or environmental considerations. If you’re looking for expert advice tailored to your requirements, get in touch with us today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Which method offers better accuracy for intricate designs?
CNC glass machining offers superior accuracy for intricate designs due to its reliance on high precision and tight tolerances. It excels at creating complex shapes, making it the ideal machining process for applications requiring exact specifications.
Is CNC glass machining more expensive than traditional methods?
The upfront costs of CNC machining, including setup and equipment, are higher than traditional methods. However, CNC machines provide durable, consistent results and are more cost-effective for custom glass fabrication in large-scale projects, balancing the investment.
What types of glass are best suited for each method?
CNC machines accommodate challenging glass types like fused silica and borosilicate, meeting the highest industry standards. Traditional machining works best for soda-lime or simpler glass varieties, where durability and complexity are less pressing.
How does turnaround time compare between CNC and traditional glass machining?
CNC machining offers faster turnaround times due to automated setup and precise ISO execution, irrespective of width or inches in component size. Traditional methods may take longer, depending on manual inputs and project complexity.
Are there environmental or safety considerations unique to either process?
Glass CNC machining uses automated measures like laser cutting, enhancing safety and reducing waste. Traditional methods require manual tools and special precautions with fragile glass types, particularly during production of pieces with varied thickness.
Related News



