Comparing Laminated Glass and Tempered Glass: Which is the Superior Option?
发布时间:
2025-05-05 16:25
来源:
Comparing Laminated Glass and Tempered Glass: Which is the Superior Option?
When it comes to selecting the right type of glass for your needs, a crucial question arises: what makes one type of glass more suitable than another for various applications?
Choosing between laminated and tempered glass can be challenging without understanding their differences. Both types have unique properties that make them ideal for different uses, from enhancing safety to improving energy efficiency.
Huize Glass, a renowned expert in the field, offers insights into the characteristics of each glass type. Understanding these can help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the primary differences between laminated and tempered glass.
- Learn about the safety features of each glass type.
- Discover the best applications for laminated and tempered glass.
- Gain insights from Huize Glass's expertise in glass manufacturing.
- Make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
Understanding Glass Safety Technologies
As the demand for safer and more resilient buildings grows, the importance of understanding glass safety technologies cannot be overstated. The role of glass in modern construction has evolved significantly, with a heightened focus on safety and impact resistance.
The Importance of Safety Glass in Modern Construction
Safety glass, including laminated and tempered glass, plays a crucial role in enhancing building safety. Laminated glass, for instance, is known for its ability to hold together upon impact, reducing the risk of injury from sharp edges. This characteristic makes it an ideal choice for applications where safety is paramount.
The use of safety glass is not just a best practice; it's often mandated by building codes. For example, many jurisdictions require the use of impact resistance glass in areas prone to severe weather conditions or in high-rise buildings.
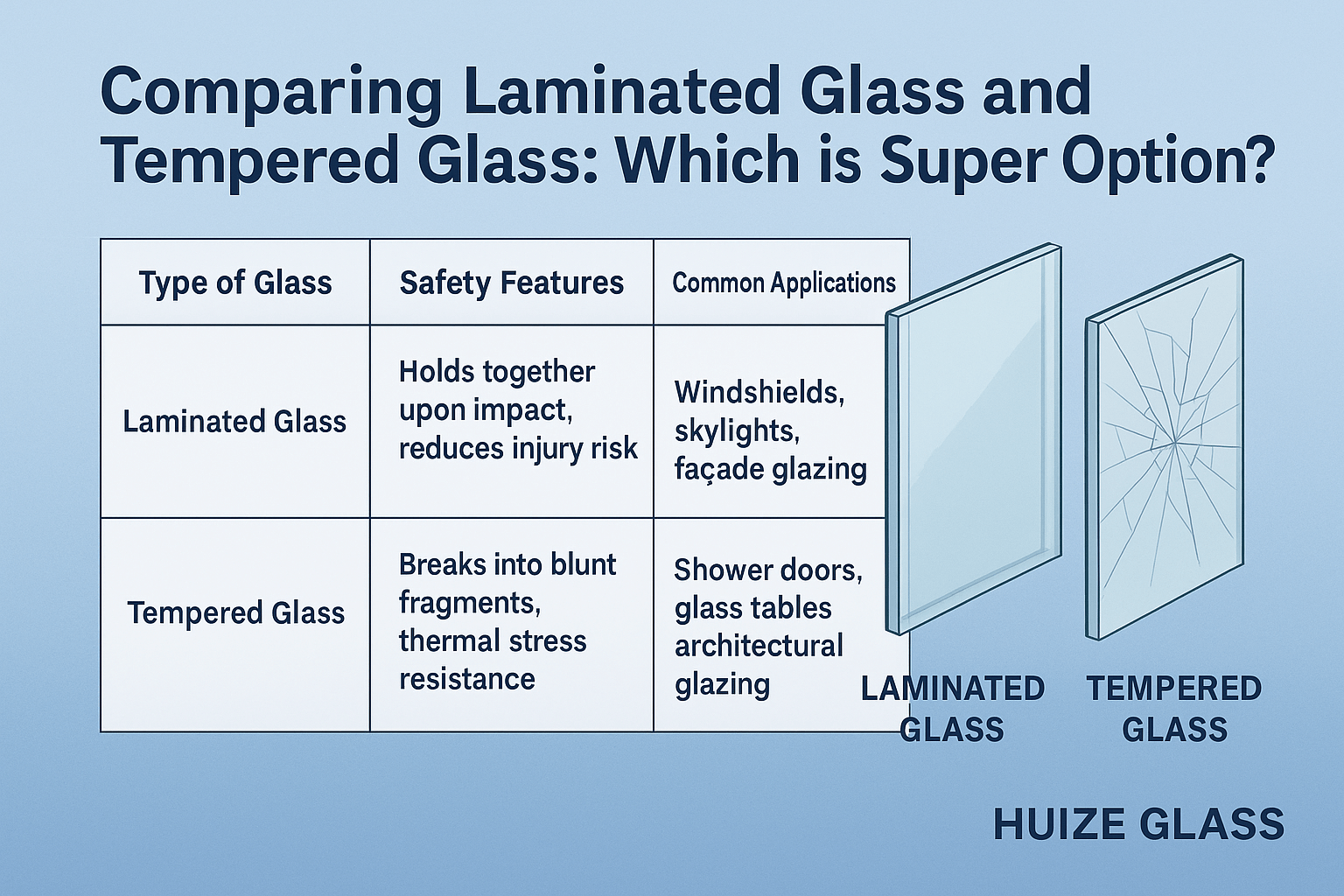
| Type of Glass | Safety Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Laminated Glass | Holds together upon impact, reduces injury risk | Windshields, skylights, façade glazing |
| Tempered Glass | Breaks into blunt fragments, thermal stress resistance | Shower doors, glass tables, architectural glazing |
Evolution of Glass Safety Standards
Glass safety standards have evolved over the years, driven by advances in technology and a deeper understanding of glass behavior under various conditions. As noted by a leading industry expert, "The development of safety glass has been pivotal in reducing injuries and enhancing building safety."
"The development of safety glass has been pivotal in reducing injuries and enhancing building safety."
This evolution is reflected in the glass comparison between older and newer glass technologies, highlighting significant improvements in safety and performance. When selecting glass for a project, understanding these standards is crucial for making an informed decision about the best glass for safety.
What is Laminated Glass?
In the realm of glass technology, laminated glass stands out for its unique properties. Laminated glass is a type of safety glass that is made by sandwiching a layer of plastic, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), between two or more layers of glass. This construction provides laminated glass with its characteristic strength and durability.
The use of laminated glass is widespread in applications where safety and security are paramount, such as in vehicle windshields and architectural glass installations. Its ability to hold together when shattered reduces the risk of injury from sharp glass fragments, making it an essential component in modern construction and automotive design.
Manufacturing Process of Laminated Glass
The manufacturing process of laminated glass involves several precise steps. First, two or more sheets of glass are cleaned and prepared. A layer of PVB is then placed between these sheets, and the assembly is subjected to heat and pressure in an autoclave, bonding the layers together. This process ensures a strong and durable final product.
Key Properties and Characteristics
Laminated glass offers several key benefits, including enhanced safety, security, and sound insulation. Its ability to remain intact even when broken makes it ideal for applications where safety is a concern. Additionally, laminated glass can be designed to provide UV protection and can be used in a variety of architectural and automotive applications.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass, known for its strength and durability, is a type of safety glass processed by heat treatment. This process involves heating the glass to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it, a technique known as quenching.
Manufacturing Process of Tempered Glass
The manufacturing process of tempered glass begins with cutting the glass to the desired size. The glass is then heated in a tempering oven to a temperature of around 600°C (1112°F). Once heated, the glass is rapidly cooled using jets of air, a process that strengthens the glass by creating compressive stresses on its surface.
This tempering process gives the glass its enhanced strength and durability, making it more resistant to thermal stresses and impacts.
Key Properties and Characteristics
Tempered glass has several key properties that make it a preferred choice in various applications. Some of its notable characteristics include:
- Enhanced Strength: Tempered glass is several times stronger than regular glass, making it more resistant to impacts.
- Thermal Resistance: It can withstand significant temperature changes without breaking.
- Safety: When tempered glass breaks, it shatters into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing the risk of injury.
These properties make tempered glass an ideal choice for applications where safety and durability are paramount, such as in architectural glass installations, vehicle windshields, and shower doors.
Which is Better, Laminated Glass or Tempered Glass?
To determine which glass type is superior, it's essential to compare laminated and tempered glass across various parameters. Both types have their unique strengths and are suited for different applications.

Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Laminated glass is known for its impact resistance, holding together even when broken due to its interlayer. This makes it ideal for applications where safety and security are paramount. Tempered glass, on the other hand, is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces, reducing the risk of injury. While it is strong, it doesn't remain intact upon impact.
Safety Performance During Breakage
In terms of safety performance during breakage, both glasses have their advantages. Laminated glass remains in the frame, preventing debris from falling, whereas tempered glass, although it breaks into safer fragments, can still cause injury if the shards are large enough.
Durability and Longevity Factors
When considering durability and longevity, laminated glass tends to have an edge due to its protective interlayer, which shields it from environmental factors. Tempered glass, while durable, can be more prone to scratches and edge damage.
In conclusion, the choice between laminated and tempered glass depends on the specific needs of the project, including factors like impact resistance, safety during breakage, and overall durability.
Pros and Cons Analysis
To make an informed decision, it's essential to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of both laminated and tempered glass. This analysis will help you understand the trade-offs involved in choosing one type over the other for your specific needs.
Pros and Cons of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass offers several advantages, including enhanced safety and security due to its ability to hold together when broken. It also provides UV protection by blocking harmful ultraviolet rays, which can damage furnishings and flooring. However, laminated glass is generally more expensive than tempered glass and may require additional framing to accommodate its weight and size.
The benefits of laminated glass include its ability to reduce noise pollution and provide structural integrity. On the downside, it can be heavier and more challenging to install than tempered glass.
Pros and Cons of Tempered Glass
Tempered glass, on the other hand, is known for its strength and durability, making it resistant to thermal stress and impact. It is also generally less expensive than laminated glass. However, once tempered glass is broken, it shatters into small, sharp pieces, which can be hazardous.
The advantages of tempered glass include its thermal resistance and aesthetic appeal. Nevertheless, it lacks the security features of laminated glass, as it does not hold together when broken.
Ideal Applications for Each Glass Type
When it comes to choosing the right glass for your project, understanding the ideal applications for laminated and tempered glass is crucial. Both types of glass have unique properties that make them suitable for different uses.
Laminated glass, for instance, is known for its safety and security features. It is made by sandwiching a layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) between two glass panes, which holds the glass together in the event of breakage.
Best Uses for Laminated Glass
Laminated glass is ideal for applications where safety and security are paramount. Some of the best uses for laminated glass include:
- Windshields and skylights
- Glass floors and walkways
- Security glass for banks and jewelry stores
Best Uses for Tempered Glass
Tempered glass, on the other hand, is known for its strength and durability. It is made by heating the glass to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it, which increases its resistance to thermal stress.
Some of the best uses for tempered glass include:
- Shower doors and glass tables
- Glass railings and balustrades
- Oven doors and fireplace screens
Choosing Glass for Windows and Doors
When it comes to choosing glass for windows and doors, both laminated and tempered glass can be suitable options. However, the choice ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your project.
For example, if you're looking for a glass that provides additional security and soundproofing, laminated glass may be the better choice. On the other hand, if you're looking for a glass that is highly resistant to thermal stress, tempered glass may be the way to go.
How to Choose the Right Glass for Your Project
The process of selecting the ideal glass for your project involves evaluating your needs, understanding the options, and making a well-informed choice. With laminated and tempered glass being the most common types, understanding their characteristics is key. This section will guide you through the decision-making process.
Step1: Assess Your Safety and Security Requirements
Begin by assessing your project's safety and security needs. Consider the risk of injury from breakage and the potential for forced entry. If safety is a top concern, laminated glass is often the preferred choice due to its ability to hold together upon impact.
Step2: Consider Environmental Factors and UV Protection
Next, consider the environmental factors that may affect your glass choice, such as exposure to sunlight and extreme weather conditions. Laminated glass also offers superior UV protection, making it ideal for applications where fading of interiors is a concern.
Step3: Evaluate Budget Constraints and Long-term Value
Evaluate your budget and consider the long-term value of your glass choice. While tempered glass may be more cost-effective upfront, laminated glass can offer greater durability and lower maintenance costs over time.
Step4: Consult with Glass Professionals for Compliance
Finally, consult with glass professionals to ensure your chosen glass complies with local building codes and regulations. They can provide valuable insights tailored to your project's specific needs, helping you make the best choice for your needs.
Conclusion
When deciding between laminated and tempered glass, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of your project. The comparison between laminated vs tempered glass reveals that each type has its unique advantages and ideal applications.
Laminated glass offers superior safety and security features, making it an excellent choice for applications where impact resistance is crucial. On the other hand, tempered glass provides enhanced strength and thermal resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of uses, including shower doors and glass tables.
A thorough glass comparison highlights the importance of assessing your project's specific needs, including safety, security, and environmental factors. By understanding the properties and characteristics of laminated and tempered glass, you can make an informed decision that meets your needs and budget.
Ultimately, the choice between laminated and tempered glass depends on your specific requirements. By considering factors such as safety, durability, and aesthetics, you can select the most suitable glass type for your project, ensuring a successful outcome.
FAQ
What is the main difference between laminated glass and tempered glass?
Laminated glass is made by sandwiching a layer of plastic between two layers of glass, while tempered glass is made by heat-treating glass to increase its strength and durability. The main difference lies in their manufacturing process and properties.
Which type of glass is more resistant to impact?
Laminated glass is generally more resistant to impact due to its layered structure, which helps to absorb and distribute the force of the impact. Tempered glass, on the other hand, is more prone to shattering into small pieces when broken.
Is laminated glass or tempered glass better for safety?
Both laminated and tempered glass have their own safety benefits. Laminated glass remains intact even when broken, reducing the risk of injury from sharp edges. Tempered glass, while it shatters into small pieces, is less likely to cause injury due to its blunt fragments.
Can laminated glass and tempered glass be used together?
Yes, laminated and tempered glass can be used together to create a glass product that combines the benefits of both types. For example, laminated tempered glass is a type of glass that is both tempered and laminated, offering enhanced strength and safety.
How do I choose between laminated glass and tempered glass for my windows?
The choice between laminated glass and tempered glass depends on your specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as safety, security, environmental conditions, and budget constraints to make an informed decision.
Are there any specific building codes or regulations that govern the use of laminated glass and tempered glass?
Yes, there are building codes and regulations that specify the use of laminated glass and tempered glass in certain applications. Consult with glass professionals and local authorities to ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Can laminated glass and tempered glass be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, both laminated glass and tempered glass can be customized to meet specific requirements, such as size, shape, color, and thickness. Consult with glass manufacturers like Huize Glass to explore customization options.
Related News




